What does it actually look like deep inside our ears? This is has been very difficult to study as the inner ear is protected by the hardest bone in the body. But with the help of synchrotron X-rays, it is now possible to depict details inside the ear, three-dimensionally. Together with Canadian colleagues, researchers from Uppsala University have used the method to map the blood vessels of the inner ear. A summary of the research appears on the Uppsala University website.
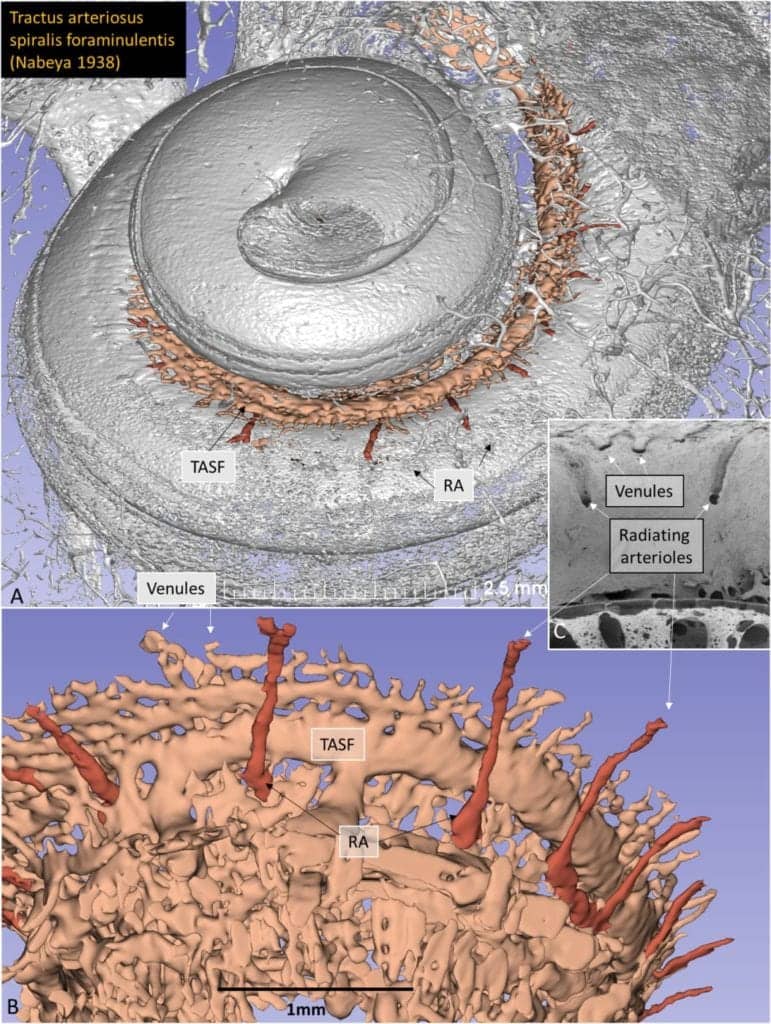
The study, published in the scientific journal Scientific Reports, can provide an explanation for why it is so effective to treat deafness in people with cochlear implants (CI). This is a method that uses an electrode to electrically stimulate the auditory nerve. To-date, around 500,000 people worldwide have been treated with this technique. In Uppsala, the operation is also performed on patients with severe hearing loss who can perceive sounds with lower frequencies.
“We need to get better at understanding the microanatomy of the human auditory organ and how electrodes operated in affect structures in the cochlea,” said Helge Rask-Andersen, senior professor in experimental otology at the Department of Surgical Sciences. “It can lead to an improved electrode design and better hearing results. Three-dimensional reconstructions mean that we can study new surgical paths to the auditory nerve.”
To be able to study the blood vessels in the inner auditory organ, the researchers used a synchrotron system from Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada. The system, which is one of eight in the world, is as large as a football pitch and accelerates particles with very high energy. This makes it possible to create pictures of the smallest parts of the inner ear. Through computer processing, the images can then be made three-dimensional.
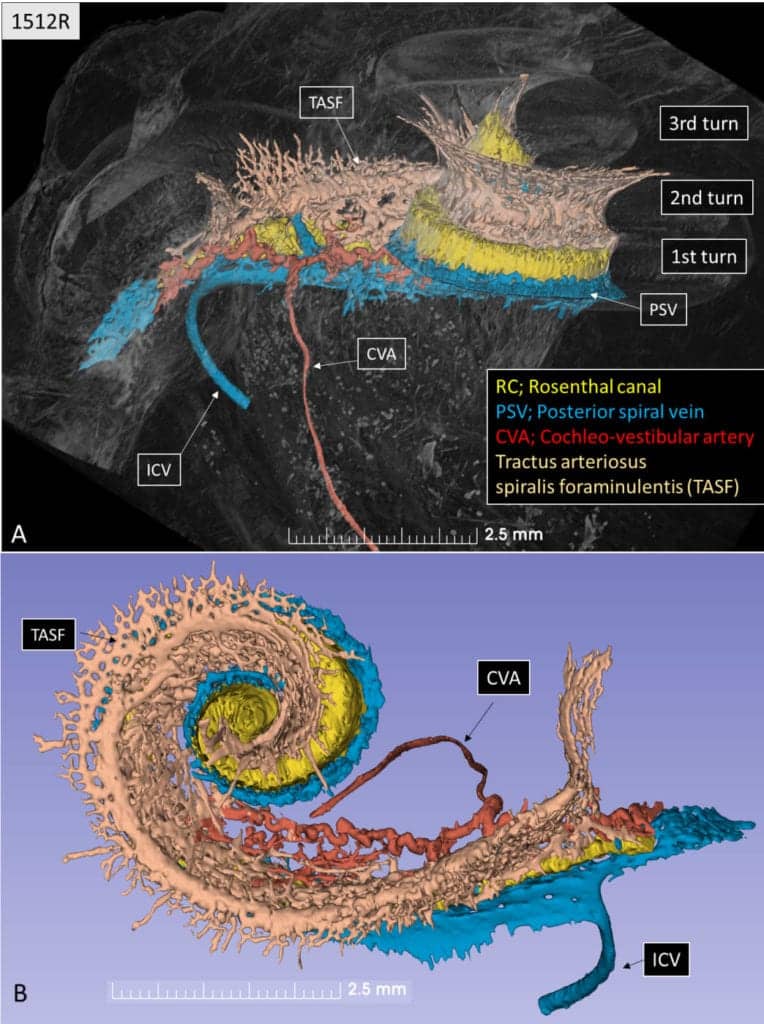
The researchers hope the method in the future can contribute to new knowledge about diseases of the ear, such as Meniere’s disease, sudden deafness, and tinnitus, the causes of which are still largely unknown. But, as yet, it is not possible to study living patients with this technique, as the radiation is too strong.
“We study specimens from the deceased, meaning donated temporal bones. We hope that the technology can be modified in the future to achieve better resolution than today,” said Rask-Andersen.
Original Paper: Mei X, Glueckert R, Schrott-Fischer A, et al. Vascular supply of the human spiral ganglion: novel three-dimensional analysis using synchrotron phase-contrast imaging and histology. Scientific Reports. 2020;10(5877):1-10.
Source: Uppsala University, Scientific Reports
Images: Uppsala University





