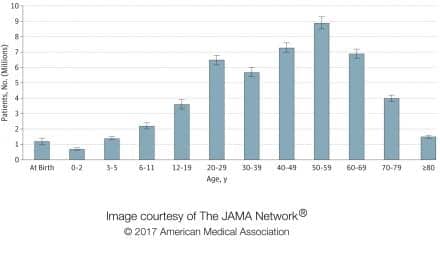
Bottom Line: Age-related hearing loss may be a risk factor for cognitive decline, impairment, and dementia, JAMA Network announced on its website.
Why The Research Is Interesting: Age-related hearing loss is common. Research about a link between age-related hearing loss and cognitive decline and dementia has been inconsistent. Understanding any possible association between hearing loss and cognitive decline could help with strategies to prevent cognitive decline and dementia with use of hearing assist devices.
Who: 20,264 participants in 36 studies
What (Study Measures): Age-related hearing loss (exposure) and measures of cognitive function, cognitive impairment, and dementia (outcomes).
How (Study Design): This was a systematic review and meta-analysis. A meta-analysis combines the results of multiple studies identified in a systematic review and quantitatively summarizes the overall association between the same exposure and outcomes measured across all studies.
Authors: David G. Loughrey, BA (Hons), Trinity College, Dublin, Ireland and coauthors.
Results: There was a small association between age-related hearing loss and increased risk for cognitive decline (such as in executive function, episodic memory, and processing speed), cognitive impairment, and dementia.
Study Limitations: The studies analyzed were observational and cannot prove a cause-and-effect relationship.
Related material: The following related elements also are available on the For The Media website:
- The editorial, “Sensory Changes and the Hearing Loss-Cognition Link,” by Francesco Panza, MD, PhD, University of Bari “Aldo Moro,” Bari, Italy, and coauthors.
Previously published by JAMA Internal Medicine: Hearing Loss and Cognitive Decline in Older Adults
Original Paper: Loughrey DG, Kelly ME, Kelley GA, Brennan S, Lawlor BA. Association of age-related hearing loss with cognitive function, cognitive impairment, and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery. December 7, 2017. doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2017.2513
Source: JAMA Internal Medicine, JAMA Network